- Dysphagia, or difficulty in swallowing food
- Regurgitation of indigested food, and later, liquid
- Coughing, especially when lying down
- Chest pain, similar to heartburn, which can be confused with a heart attack
- Aspiration, when food, liquid, and saliva are inhaled into the lungs
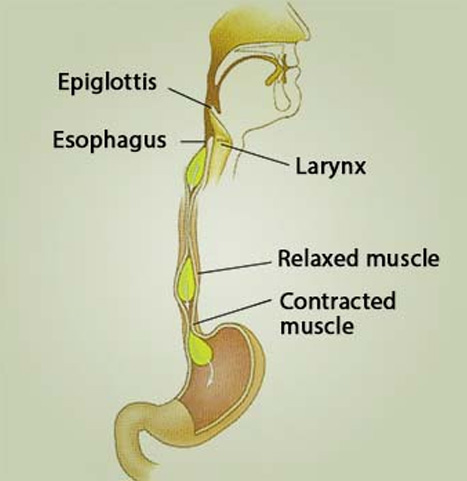
The person may also lose weight, have difficulty burping and feel as if they have a lump in their throat.
Symptoms are usually mild and ignored at first, and people may try to compensate by eating more slowly or by lifting the neck or throwing the shoulders back to help them swallow.
However, symptoms typically get progressively worse.
Treatment
Treatment cannot cure achalasia or restore the nerve function, but it can reduce symptoms.
Medications: If diagnosis is made early, medications can help dilate the narrowed part of the esophagus so that food can pass through properly. Examples include calcium channel blockers and nitrates. Some patients may experience headaches and swollen feet, and after some months, some medications stop working.
Balloon, or pneumatic, dilation: A small balloon is passed into the narrowed section and inflated to widen the space by tearing the muscle in the lower esophageal sphincter. This may need to be done more than once. For about 60 percent of patients, one balloon treatment is sufficient for a year, and for around 25 percent, the effects last for 5 years.
Complications include chest pain immediately after the procedure, and a small risk of perforating the esophagus, which will need further treatment. Balloon dilation also leads to GERD in about 2 percent of patients.
Myotomy: An operation to cut the muscle usually helps prevent obstruction. It has a success rate of between 70 percent and 90 percent. Symptom relief will last for 10 years in 85 percent of cases, and 65 percent of people will have relief for 20 years.
Peroral endoscopy myotomy (POEM): The surgeon passes an electrical scalpel through an endoscope, makes an incision in the lining of the esophagus and creates a tunnel within the esophageal wall. This procedure appears to be safe and effective, but its long-term effects are unknown, as it is a relatively new procedure.
Botox: This can be given as injections to relax muscles on the lower part of the esophagus. Botox injections can help those who are unable or unfit to undergo surgery. A single injection provides relief for 3 months in 65 to 90 percent of patients, but then it must be repeated.
Following non invasive surgery, the patient can expect to spend between 24 hours and 48 hours in the hospital and to return to normal activities after 2 weeks. A person who undergoes open surgery will probably need a longer hospital stay, but they will be up and about in 2 to 4 weeks.
After surgery or some procedures, proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) may help prevent gastric acid secretion, and this can prevent reflux.
Complications
Since achalasia cannot be cured, patients should seek regular followup to detect and treat any complications in the early stages.
Acid reflux, severe enlargement of the esophagus, known as mega-esophagus, and squamous-cell esophageal cancer are all possible complications.Some experts suggest using endoscopy to screen for these complications once every 3 years in people who have had achalasia for at least 10 to 15 years.




