Surgery:
Gastric bypass surgery is performed under general anaesthesia. Your surgeon makes several small incisions on your abdomen. A laparoscope, a thin instrument with a light and camera on the end, is inserted through one of the incisions, allowing your surgeon to clearly view the internal organs on a monitor. Small surgical instruments are inserted through the other incisions to perform the surgery.
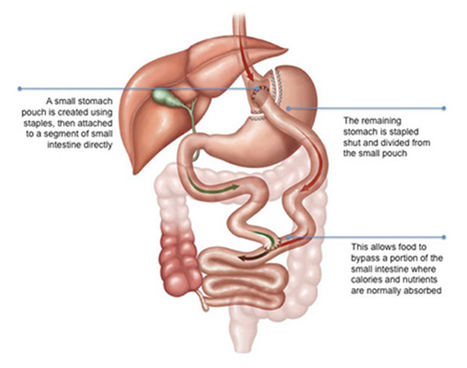
The first step is to reduce the size of the stomach so that it holds less food. The upper portion of the stomach near the oesophagus is converted into a pouch by stapling.
The second step of the surgery involves the creation of a bypass for food to flow from the new stomach pouch. The small intestine is divided into upper and lower segments.
The lower section of intestine is attached to the opening in the stomach pouch creating what is referred to as the “rouxlimbâ€. The upper section of the small intestine which carries digestive juices from the remaining portion of the stomach is attached at the distal end of the roux limb. The roux limb enables food to bypass the lower stomach, duodenum, and a portion of the small intestine. At the end of the procedure, the incisions are closed with sutures
 Post-operative care:
Post-operative care:
After gastric bypass surgery, you will have to stay in the hospital for about 3 to 5 days.
Your doctor will prescribe pain relieving medications to keep you comfortable. You will be given instructions to follow regarding wound care, diet and activity such as:
- Keep the incision area clean and dry.
- Avoid strenuous exercises and lifting heavy weights. But you will be instructed to start walking and remain active.
- You will be put on liquid diet post-surgery for 10 to 15 days followed by soft diet.
- Sip water throughout the day to prevent dehydration.
- Follow the diet regimen given to you by the dietician.
- Follow an exercise program per your surgeon’s instructions to maintain the weight loss.
Advantages
Gastric bypass surgery can help you lose about 5 to 10 kilograms a month in the first year following surgery. You will gradually lose more weight by eating a healthy diet and participating in regular exercise. The surgery also helps you manage obesity-related health conditions.
Disadvantages:
- It is not possible to fully reverse the procedure due to partial removal of the stomach.
- Lifelong follow up with a physician is required for blood tests to ensure proper health and nutrition.
Risks and Complications:
As with any surgery there are potential risks and complications involved. Complications associated with Gastric Bypass include:
- Problems associated with anaesthesia
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Bowel obstruction
- Leaks in your gastrointestinal tract
- Deep vein thrombosis (blood clot in the leg)
- Dumping syndrome leading to diarrhoea and nausea
- Hernia
- Gallstones
- Malnutrition
- Ulcers




 Post-operative care:
Post-operative care: