Prolonged blockage of a bile duct can cause a buildup of waste products in the biliary tract and in the bloodstream, leading to an infection called cholangitis. It also can prevent the release of bile into the small intestine to help digest food or cause a serious bacterial infection in the liver called ascending cholangitis.
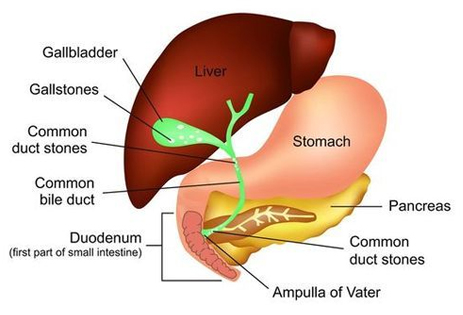 A blocked bile duct may result in inflammation of the gallbladder, called cholecystitis. A gallstone or bile stone in the common bile duct may block the pancreatic duct, causing painful inflammation of the pancreas or pancreatitis.
A blocked bile duct may result in inflammation of the gallbladder, called cholecystitis. A gallstone or bile stone in the common bile duct may block the pancreatic duct, causing painful inflammation of the pancreas or pancreatitis.
If a stone completely blocks the ducts of the gallbladder, liver, common bile duct or pancreas, other symptoms may include:
- Nausea
- Fever
- Chills
- Yellow skin or eyes (from the build up of bilirubin, a waste product in blood)
- Dark urine
- Itching
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
- Night sweats
- Loss of appetite
- Greasy or light-colored stools
Diagnosing Gallstones and Bile Duct Stones
Your gastroenterologist can diagnose and treat gallstones and bile duct stones at the same time with minimally invasive endoscopic technology. Common diagnostic tests and procedures for confirming the presence of stones include:
- Blood Tests
- Abdominal Ultrasound
- Abdominal Ct Scan
- ERCP
- ERCP With Endoscopic Ultrasound
- MRCP
Treatment:
Mainstay of treatment is removal of stone. This can be done by various techniques depending on the condition of the patient and size of stone. The options are:
1. ERCP
2. Laparoscopic Common Bile duct exploration
3. Open common bile duct exploration




 A blocked bile duct may result in inflammation of the gallbladder, called cholecystitis. A gallstone or bile stone in the common bile duct may block the pancreatic duct, causing painful inflammation of the pancreas or pancreatitis.
A blocked bile duct may result in inflammation of the gallbladder, called cholecystitis. A gallstone or bile stone in the common bile duct may block the pancreatic duct, causing painful inflammation of the pancreas or pancreatitis.