1. Immune system
There is a possibility that a virus or bacterium may aggravate the disease. Here the immune system fights the invading microorganism, then an abnormal immune response causes it to attack the cells in the digestive tract, too.
2. Heredity
The people who are more prone to Crohn's disease generally have a family history with the members suffering from the disease.
Symptoms of Crohn’s disease
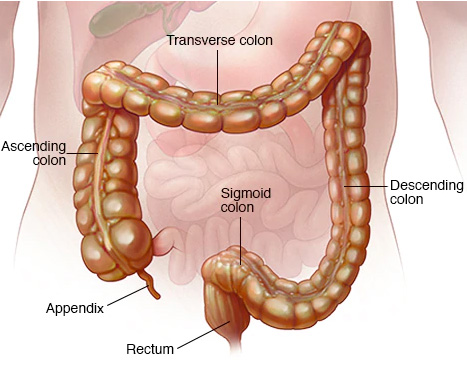
In Crohn’s disease, mostly the last segment of the small intestine (ileum) is affected. But in some people, the disease is confined to the colon which is the part of the large intestine. However, the most common areas affected by it are the last part of the small intestine and the colon. The signs and symptoms usually range from mild to severe.
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Diarrhoea
- Chronic constipation
- Bleeding with bowel movements
- Fever & Fatigue
- Weight loss and reduced appetite
- Drainage from the skin around the anus
- Anal fissures
- Feeling of pain near or around the anus
- Mouth sores
There are other signs and symptoms as well like Inflammation of skin, eyes, joints and liver and delayed growth or sexual development in children.
Diagnosis of Crohn’s disease
Apart from examining the symptoms, the doctor uses a combination of tests to confirm a diagnosis of Crohn's diseases like;
1. Blood test
The test is done to check whether the patient is suffering from anaemia or any other infection. The other test could be a faecal occult blood test by providing the stool sample.
2. Procedures
Colonoscopy, CT scan, Capsule endoscopy, MRI and Balloon-assisted enteroscopy all these test procedures are undertaken by the patient which targets the different parts of the affected area to be examined.
Treatment of Crohn’s disease
1. Medical treatment
The goal of medical treatment is to reduce the inflammation that enhances the symptoms of the disease. The intake of medicine limits the complications thus, leading not only to symptom relief but also to long-term remission.
Anti-inflammatory drugs
The consumption of anti-inflammatory drugs which are considered to be very effective is the first step in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Like Corticosteroids, Oral 5-aminosalicylates etc.
Immune system suppressors
The objective of immune system suppressor is to reduce inflammation, but they target your immune system, which produces the substances that cause inflammation. This includes Azathioprine and mercaptopurine, Methotrexate etc.
Other medicines include antibiotics, pain relievers, Anti-diarrheals etc. Sometimes, these medications too complement the anti-inflammatory drugs in reducing the symptoms of Crohn’s disease.
2. Surgical treatment
Surgery becomes mandatory when the patient suffering from the disease is unable to control the symptoms by medications and lifestyle and diet changes. This majorly entails the removal of the damaged portion of the digestive tract and then reconnecting the healthy sections. The surgery may be also be needed when patients develop disease-related abdominal and anorectal complications.
Abdominal surgery
The surgery can be performed by two approaches either by a traditional open approach or through a minimally invasive procedure. However, in the case of an emergency, abdominal surgery is undertaken as an open procedure due to the urgency of the situation. Here, the surgeon decides the safest approach based on the individual case.
Anorectal surgery
The surgery is opted to open and drain anorectal abscesses. A seton (small drain) may be left in place for a period of time until the infection clears up. Surgery is also used to treat anorectal fistulas.
Post- treatment prognosis
After the surgery it is very imperative to keep an eye over the symptoms and to follow up with the doctor so, they can devise an ongoing management plan to control them. One cannot completely get rid of the disease, basically, management of it works. There is long term medication as it increases the risk of colon cancer.
How to reduce reoccurrence?
Long term medication and management what it needs as recurrence is most common in patients of Crohn’s disease if they stop taking their medicines, so here becomes important to follow the doctor’s orders. Also, it is often advised to avoid smoking as it has been linked to higher recurrence rates.